Lan Biomedical Analysis Glossary
Lan Biomedical Analysis Glossary
20 Essential biology terms terms
Let me introduce myself. My name is Lan Tran. I have been studying Biomedical Analysis for two years at Saint-Jerome College. It's fascinating as the program. We do a laboratory every week. There are a lot of specialties in this formation. My field study is all techniques in a relation which biology and laboratory. This technique helps to prevent disease, maintain and improve health through the analysis of samples taken from patients. It has been difficult for me to star without anything, so I created this glossary to help others. In this glossary, there are 20 basic notions of biology from A to T. Although, learning the meaning of these words can help you have more confidence and take the courses easier.
- acclimatization
- Noun
- Adaptation to a new climate, to another atmosphere, similarly as with another temperature or elevation or condition.
- fr: Acclimatisation

- action potential
- Noun
- The charge in voltage that occurs when the membrane potential of a specific location along the membrane of a muscle cell or nerve cell rapidly depolarizes.
- fr: Potentiel d'action

- adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
- Noun
- An organic compound derived from adenine that functions as the major source of energy for chemical reactions inside living cells.
- fr: Adénosine triphosphate

- aerobic
- Adjective
- Capable of surviving and growing in the presence of oxygen.
- Example: The cellular respiration is aerobic.
- fr: Aérobique

- anaerobic
- Adjective
- Capable of surviving and growing in the absence of free oxygen.
- Example: Many bacteria do not require oxygen to grow.
- fr: Anaérobique
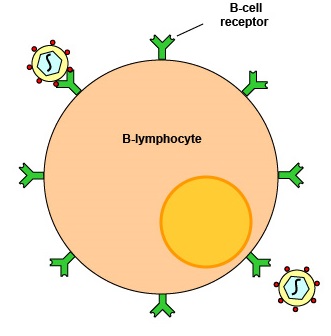
- B cell or B lymphocytes
- Noun
- A kind of white platelet of the little lymphocyte subtype emitting antibodies.
- fr: Lymphocytes B
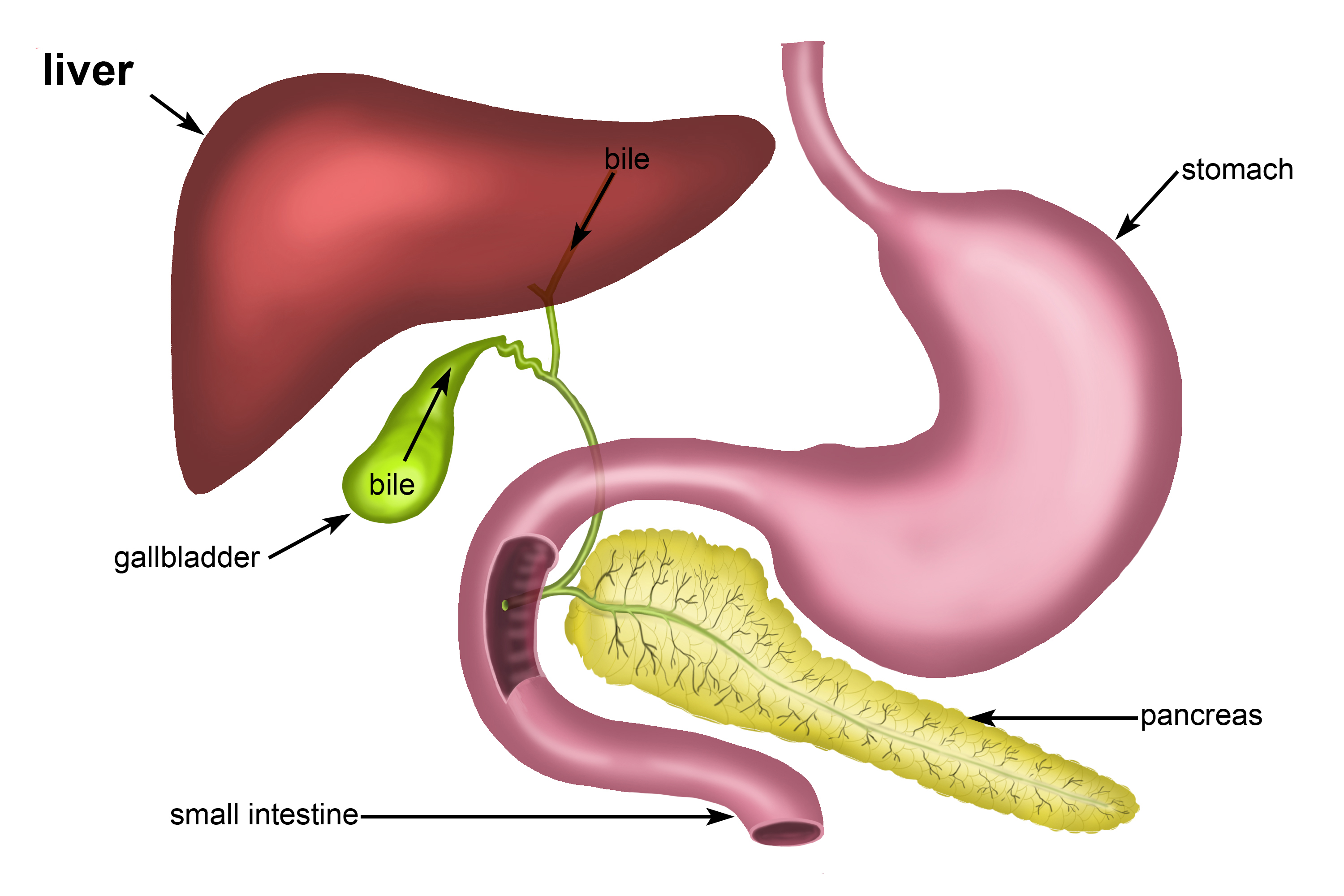
- bile
- Noun
- A dark green to yellowish-brown fluid, produced by the liver of most vertebrates, which aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine.
- fr: Bile
- blastocyst
- Noun
- A mammalian blastula in which some differentiation of cells has happened.
- fr: Blastocyste

- blood
- Noun
- The fluid that circulates in the heart, capillaries, and veins of a vertebrate animal carrying nourishment and oxygen to and bringing away waste products from all parts of the body
- fr: Du sang

- blood pressure
- Noun
- The pressure of the blood in the circulatory system, often measured for diagnosis since it is closely related to the force and rate of the heartbeat and the diameter and elasticity of the arterial walls.
- fr: Pression artériel

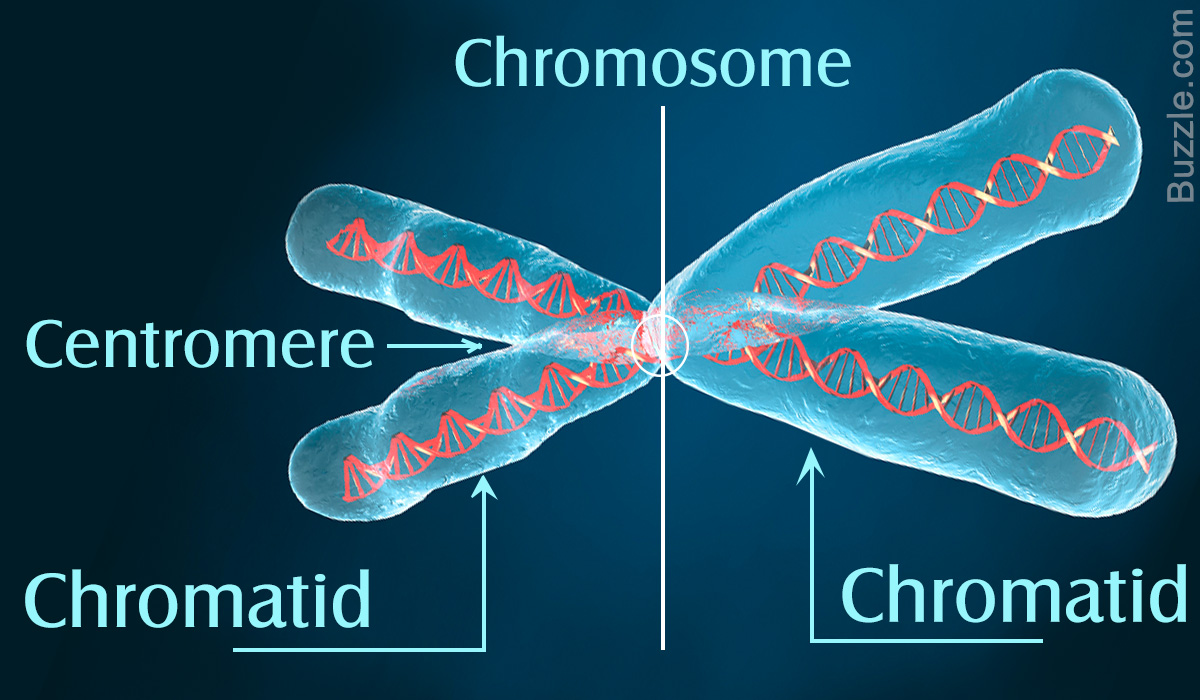
- chromosome
- Noun
- A threadlike strand of DNA in the cell nucleus that carries the genes in a linear order.
- fr: Chromosome
- coma
- Noun
- A state of unconsciousness from which a person cannot be aroused; fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound; lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle; and does not initiate voluntary actions.
- fr: Coma

- deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
- Noun
- A nucleic acid polymer that serves as the fundamental hereditary material in all living organisms. A set of four bases is used in the nucleotide sequences which comprise each DNA molecule: adenine (abbreviated A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T).
- fr: Acide désoxyribonucléique (ADN)

- erythrocyte
- Noun
- A red blood cell that made in borne. Erythrocytes contain the pigment hemoglobin and transport oxygen and carbon dioxide to and from the tissues.
- fr: Érythrocyte

- fever
- Noun
- When a rise of human body temperature goes above the normal.
- fr: Fièvre

- hemorrhage
- Noun
- An escape of blood from a ruptured blood vessel
- fr: Hémorragie

- hyperventilate
- Verb
- To breathe at an abnormally rapid rate, so increasing the rate of loss of carbon dioxide. Sometimes resulting in cramp and dizziness.
- fr: Hyperventiler
- inflammation
- noun
- The physical reaction of living tissue to injury or infection. Inflammation is part of the body's immune response.
- fr: Inflammation

- leukocyte
- Noun
- A type of blood cell that is made in the bone marrow and found in the blood and lymph tissue
- fr: Leucocyte

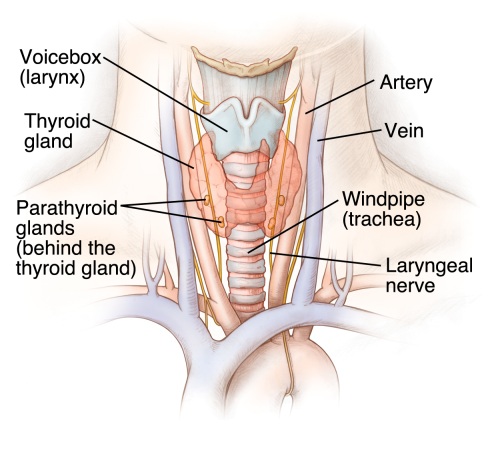
- thyroid gland
- Noun
- A large ductless gland in the neck which secretes hormones regulating growth and development through the rate of metabolism.
- fr: Glande thyroïde